US farm subsidy policies contribute to worsening obesity trends
Agricultural subsidies are responsible for making those processed and energy-dense foods that contribute to the American epidemic of obesity the most affordable options for consumers, concludes a new study led by Dr. Mark J. Eisenberg, a cardiologist and epidemiologist at the Lady Davis Institute at the Jewish General Hospital in Montreal. As Congress debates a new Farm Bill that will determine agricultural policy for the next five years, it is critical that public health be factored into legislation that will define the country’s nutritional environment.
“Tackling the policies that translate into food production and availability could be the most widespread preventive measure to address the obesity epidemic,” according to Caroline Franck, lead author of the paper published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
While many factors contribute to obesity, the ready availability and low cost of unhealthy foods in comparison with healthy alternatives are crucial. Indeed, obesity has been closely associated with poverty. Grocery stores and restaurants sell foods made from cheap commodities at lower prices, and commodities used in high fat and sweetened foods are artificially cheap because government subsidies have made the crops used to produce them lucrative to grow.
Citing statistics from 2004, the study notes that 96% of American cropland is dominated by eight main crops, including soybean and corn. The former is the source of 70% of the fats and oils consumed by Americans, while the latter is a high calorie component of soft drinks, fruit drinks, canned fruits, condiments, baked goods, and ice cream, all of which contribute to obesity.
Recognizing that farm subsidies are an important safety net for a volatile industry, Franck and her co-authors propose that agriculture policy take public health into account when identifying how they ought to be dispensed. They recommend investing in sustainable agriculture that emphasizes biodiversity, quality foods, optimizing non-renewable resources, and sustaining the economic viability of farmers. Farmers should be encouraged to grow fruits and vegetables in place of produce used for sweeteners and hydrogenated oils.
“A successful reorganization of the American food environment will require commitment to mutually supportive interventions affecting food availability, price, marketing, and health education, at the local, state, and federal levels of government,” Franck wrote. “A revision of agricultural priorities is in order: public health interventions will remain limited in their impact until they can inform decisions that are made at every level of the American food chain, from growers to consumers.”
This set of maps, from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, offers a state-by-state look at the tremendous increase in adult obesity over the past two decades. In 1990, no state had an obesity rate higher than 15 percent. By 2010, no state had an obesity rate lower than 20 percent, and 12 states had obesity rates greater than 30 percent. 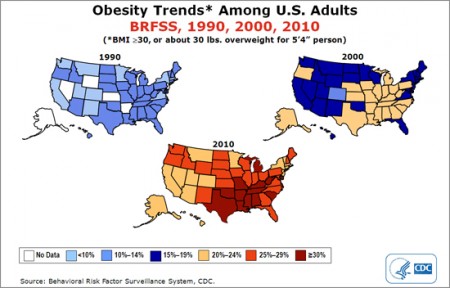
Source: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Worldwide the rate of obesity has nearly doubled since 1980, with just over 200 million adult men and just under 300 million adult women obese. Obesity rates have been steadily rising in children, too: In 2010, 43 million preschool children were overweight or obese, a 60 percent increase since 1990. And these jumps in child and adult obesity rates show no sign of stopping without dedicated efforts to combat the epidemic.
Of all high income countries, the United States has the highest rates of overweight and obesity, with fully a third of the population obese - a rate projected to rise to around 50 percent by 2030. As with most health issues, the burden of obesity isn’t felt equally across all parts of society. The poor have higher rates than those with higher income. Those with less education have higher rates than those with more education. And certain minority groups- especially African-American and Hispanic women - have much higher rates than other groups.
###
“Agricultural Subsidies and the American Obesity Epidemic” by Caroline Franck, Sonia M. Grandi, and Mark J. Eisenberg is available online as of July 9, 2013 at ajpmonline.org and in print in the September issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
###
Charlotte Seidman
.(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address)
858-534-9340
Elsevier Health Sciences