New hope for Gaucher patients
What causes brain damage and inflammation in severe cases of Gaucher disease? Little is known about the events that lead to brain pathology in some forms of the disease, and there is currently no treatment available – a bleak outlook for sufferers and their families. Now, scientists at the Weizmann Institute of Science have discovered a new cellular pathway implicated in Gaucher disease. Their findings, published today in Nature Medicine, may offer a new therapeutic target for the management of this disease, as well as other related disorders.
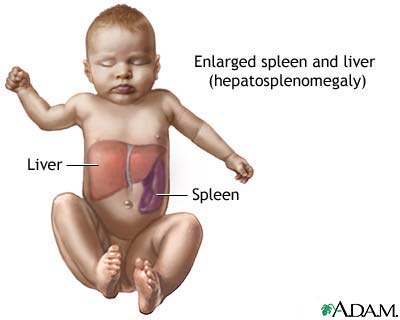
Gaucher disease is a genetic disorder most prevalent among the Ashkenazi Jewish population. It is caused by a defect in a particular enzyme needed to break down a fatty substance, or lipid, called glucocerebroside. This results in the accumulation of glucocerebroside in various cells and organs, which prevents them from working properly. There are three subtypes of the disease: The most common form - Type 1 - is characterized by, among other symptoms, swelling and enlargement of the spleen and liver and disruption in the function of these organs, along with lung and bone problems. These symptoms can also affect individuals with Types 2 and 3 Gaucher disease, but what distinguishes them from Type 1 is the neurological involvement: Type 2 - the most severe form - causes extensive brain damage and death before two years of age, while Type 3 is a more progressive form of the disease that affects the brain, with patients often living into their early teens and adulthood.
But what exactly causes such a massive loss of nerve cells in Types 2 and 3 Gaucher disease? It has recently come to light that a certain biochemical pathway, of which a protein called RIP3 is a key player, is involved in triggering the cell death and inflammatory processes that can have severe consequences in a number of diseases. Dr. Einat Vitner and M.Sc. student Ran Salomon, in the lab of Prof. Tony Futerman of the Biological Chemistry Department, wondered whether this could also be one of the missing links in the understanding of the chain of molecular events leading to brain inflammation and nerve cell death in Gaucher disease. To find out, they induced Gaucher disease in mice possessing the RIP3 protein, as well as in mice lacking RIP3. In mice lacking the RIP3 protein, they demonstrated not only a significant improvement in motor coordination and brain pathology but also improved liver and spleen function. Their lifespan was also remarkably increased from approximately 35 days to more than 170 days.
Vitner: “These results are exciting, as they suggest a plausible new target for therapeutic intervention for all types of Gaucher disease; they have the potential, in the future, to greatly improve the patients’ quality of life.”
Indeed, although effective enzyme replacement therapy exists in which Gaucher patients are treated with injections of an intact version of the enzyme responsible for the normal breakdown of the lipid in healthy people, the cost of the lifelong treatment is approximately $200,000 per patient per year. Moreover, the enzyme is unable to get into the brain since it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, rendering it ineffective in treating the neurological symptoms of Types 2 and 3 Gaucher disease. Hence, more affordable and alternative treatments are urgently needed.
Gaucher’s disease is a rare, inherited disorder in which you do not have enough of an enzyme called glucocerebrosidase. This causes too much of a fatty substance to build up in your spleen, liver, lungs, bones and, sometimes, your brain. This prevents these organs from working properly.
There are three types:
- Type 1, the most common form, causes liver and spleen enlargement, bone pain and broken bones, and, sometimes, lung and kidney problems. It does not affect the brain. It can occur at any age.
- Type 2, which causes severe brain damage, appears in infants. Most children who have it die by age 2.
- In type 3, there may be liver and spleen enlargement. The brain is gradually affected. It usually starts in childhood or adolescence.
Gaucher’s disease has no cure. Treatment options for types 1 and 3 include medicine and enzyme replacement therapy, which is usually very effective. There is no good treatment for the brain damage of types 2 and 3.
 “If successful, the new target could be used as either a complementary or alternative therapy for Gaucher disease, and with RIP3 proving to be a ‘hot’ cellular pathway in various pathologies, these results may also have implications in other neurodegenerative diseases, including related diseases such as Krabbe disease, and potentially other devastating brain diseases,” says Futerman.
“If successful, the new target could be used as either a complementary or alternative therapy for Gaucher disease, and with RIP3 proving to be a ‘hot’ cellular pathway in various pathologies, these results may also have implications in other neurodegenerative diseases, including related diseases such as Krabbe disease, and potentially other devastating brain diseases,” says Futerman.
The Children’s Gaucher Research Fund
Beginning with a memorial fund in honor of their son Gregory, who lost his life to Neuronopathic Gaucher (nGD) disease at the tender age of four, Greg and Deborah Macres have grown the Children’s Gaucher Research Fund into a nonprofit charity that has raised over $2 million since its inception in 1999. In this grassroots organization in California, 100% of the donations go directly to research – the administrative costs are covered by the Macreses themselves, and it is supported by parents who have lost their children to nGD. It has been instrumental in enabling research aimed at finding a cure for Types 2 and 3 Gaucher Disease, such as that carried out in the lab of Prof. Tony Futerman at the Weizmann Institute, as well as providing support to families of children who battle this disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of Gaucher’s disease?
A symptom is something the patient feels and describes, such as a headache, while a sign is something others can detect, e.g. a rash.
Most patients describe their first symptom as a swollen stomach. This is usually one of the first warning signs that sends patients to the doctor - an enlarged abdomen. This is because the spleen has swollen.
One of the spleen’s functions is to weed out old blood cells. When the spleen enlarges too much, sometimes to 25 times its normal size, it weeds out too many blood cells, including good ones. This can lead to anemia. Patients with insufficient blood cells suffer from fatigue, because they are not getting enough oxygen and energy. If the spleen has taken out too many platelets, which are essential for coagulation (clotting), the patient will bleed and bruise more.
People with Gaucher’s disease do not all have the same symptoms.
There are three main types of Gaucher’s disease:
Gaucher’s disease Type 1
This is the most common type accounting for approximately 9 in every 10 cases, also the one with the least severe symptoms. Patients are usually diagnosed in their late twenties to early thirties, although the disease can become apparent at any age. Signs and symptoms may include:
Anemia
Delayed puberty
Fatigue
Frequent nosebleeds
Hepatomegaly - enlarged liver
Osteopenia (bone thinning), bone fractures, and bone pain. Damage to the shoulder or hip joints are common.
Osteoporosis - demineralization of the bones
Pingueculae - yellow spots in the eyes
Splenomegaly - enlarged spleen
Thrombocytopenia - low blood platelet numbers, resulting in easy bruising and slow clotting times (easy bleeding)
Type 1 Gaucher’s disease is most prevalent in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Greg: “We began funding Tony in 2001 and are truly grateful for his commitment to pursuing something that very few scientists have had an interest in. His new discovery, which has major implications not only for neuronopathic Gaucher Disease, but potentially and quite remarkably for Krabbe Disease, gives us encouragement. We hope to be able to continue this journey so that one day, our goal is reached in the form of words from a physician to the anxious parents of a sick child – ‘Do not worry, we have a cure’.”
###
Prof. Anthony H. Futerman’s research is supported by the Nella and Leon Benoziyo Center for Neurological Diseases, which he heads; the M.D. Moross Institute for Cancer Research; and the Carolito Stiftung. Prof. Futerman is the incumbent of the Joseph Meyerhoff Professorial Chair of Biochemistry.
The Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, is one of the world’s top-ranking multidisciplinary research institutions. Noted for its wide-ranging exploration of the natural and exact sciences, the Institute is home to scientists, students, technicians and supporting staff. Institute research efforts include the search for new ways of fighting disease and hunger, examining leading questions in mathematics and computer science, probing the physics of matter and the universe, creating novel materials and developing new strategies for protecting the environment.
###
Yivsam Azgad
.(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address)
972-893-43856
Weizmann Institute of Science