Radiation Proctitis
Radiation-induced proctosigmoiditis occurs most commonly with radiation therapy for cancers of the testes, prostate, urinary bladder, cervix, and uterus (23,24). The incidence of radiation injury is higher in this region of the colon because of the relatively high doses of radiation used for tumors in the pelvic area and the relative immobility of the rectum and sigmoid colon.
The combination of external beam radiotherapy with radiation implants increases damage to the rectosigmoid and is often used for cervical and prostate cancer treatment because of greater efficacy. Clinically significant radiation proctosigmoiditis requiring therapy occurs in as many as 30% of patients acutely and 15% of patients chronically after pelvic radiation.
In 50% of patients there is acute injury with presenting symptoms of diarrhea and tenesmus without rectal bleeding occurring during radiation treatment or within 6 weeks of treatment completion.
The majority of symptoms resolve within 6 months with conservative therapy only, and flexible sigmoidoscopy usually shows normal findings or minimal nonspecific mucosal changes. Chronic injury presents with the common symptoms of rectal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding occurring from a latent period of 9 months to 2 years after completion of therapy.
This group may be managed conservatively with steroid enemas, sulfasalazine, and 5-ASA products given either orally or as a rectal enema. Some benefit has been noted in combining oral sulfasalazine with steroid enemas or in using sucralfate enemas alone.
Patients with significant rectal bleeding requiring blood transfusions have a lower spontaneous remission rate of 0% to 20%, often requiring surgery (~50%) and typically a higher rate of morbidity and mortality.
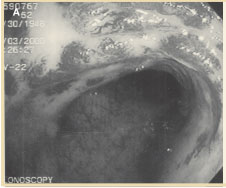
Figure 5A. Endoscopic appearance of acute radiation “proctitis.” With the advent of successful endoscopic therapy such as bipolar electrocoagulation or argon plasma coagulation, which are generally safe techniques in the hands of an experienced endoscopist, the frequency of patients requiring surgical therapy has decreased. Usually patients require multiple sessions of endoscopic therapy before clinical resolution of symptoms is attained (Figures 5A, 5B). Patients with minimal rectal bleeding requiring no transfusions have a spontaneous remission rate of >70%.
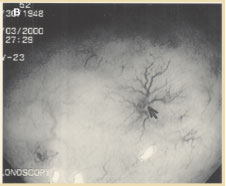
Figure 5B. Chronic radiation injury to the rectum with telangiectasias.
Deepak V. Gopal, MD, FRCP (C)
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Division of Gastroenterology
Oregon Health & Science University
Portland VA Medical Center
Portland, Oregon
REFERENCES
1. Schrock TR. Examination and diseases of the anorectum. In: Feldman M, Scharschmidt BF, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease.
2. Barnett JL. Anorectal diseases. In: Yamada T, Alpers DH, Laine L, et al, eds. Textbook of Gastroenterology. Vol 2. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999:2083 - 2107.
3. Johanson JF, Sonnenberg A. The prevalence of hemorrhoids and chronic constipation: an epidemiological study. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:380 - 386.
4. Breen E, Bleday R. Clinical features of hemorrhoids. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
5. Haas PA, Fox TA, Haas G. The pathogenesis of hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984;27:442 - 450.
6. Bleday R, Breen E. Treatment of hemorrhoids. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
7. MacRae HM, McLeod RS. Comparison of hemorrhoidal treatments: a meta-analysis. Can J Surg. 1997;40:14 - 17.
8. Reis Neto JA, Quilici FA, Cordeiro F, Reis JA. Open versus semi-open hemorrhoidectomy: a random trial. Int Surg. 1992;77:84 - 90.
9. Khubchandani M. Results of Whitehead operation. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984;27:730 - 732.
10. Breen E, Bleday R. Anal fissures. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
11. Lund JN, Scholefield JH. Aetiology and treatment of anal fissure. Br J Surg. 1996;83:1335 - 1344.
12. Shub HA, Salvati EP, Rubin RJ. Conservative treatment of anal fissure: an unselected, retrospective, and continuous study. Dis Colon Rectum. 1978;21: 582 - 583.
13. Brisinda G, Maria G, Bentivoglio AR, et al. A comparison of injections of botulinum toxin and topical nitroglycerin ointment for the treatment of chronic anal fissure. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:65 - 69.
14. Cook TA, Humphreys MM, McC Mortensen NJ. Oral nifedipine reduces resting anal pressure and heals chronic anal fissure. Br J Surg. 1999;86: 1269 - 1273.
15. Lewis TH, Corman ML, Prager ED, Robertson WG. Long-term results of open and closed sphincterotomy for anal fissure. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988;31: 368 - 371.
16. Breen E, Bleday R. Anal abscesses and fistulas. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
17. Nordgren S, Fasth S, Hulten L. Anal fistulas in Crohn's disease: incidence and outcome of surgical treatment. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1992;7:214 - 218.
18. Venkatesh KS, Ramanujam P. Fibrin glue application in the treatment of recurrent anorectal fistulas. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:1136 - 1139.
19. Gopal DV, Young C, Katon RM. Solitary rectal ulcer syndrome presenting with rectal prolapse, severe mucorrhea, and eroded polypoid hyperplasia: case report and review of the literature. Can J Gastroenterol. 2001;15:479 - 483.
20. Mackle EJ, Parks TG. The pathogenesis and patho-physiology of rectal prolapse and solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol. 1986;15: 985 - 1001.
21. Gopal DV, Faigel DO. Rectal endoscopic ultrasound - a review of clinical applications. Endoscopic ultrasonography and therapeutic indications. Series #2. Pract Gastroenterol. 2000;24:24 - 34.
22. Robson K, Lembo AJ. Fecal incontinence. Chopra S, La Mont T, eds. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
23. Nostrant TT. Radiation injury. In: Yamada T, Alpers DH, Laine L, et al, eds. Textbook of Gastroenterology. Vol 2. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999:2611 - 2612.
24. Swaroop VS, Gostout CJ. Endoscopic treatment of chronic radiation proctopathy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998;27:36 - 40.
25. Bonis P, Breen E, Bleday R. Approach to the patient with anal pruritus. [UpToDate Clinical Reference on CD-ROM & Online Web site.] December 2001.
26. American Joint Committee on Cancer. Manual for Staging of Cancer. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: JB Lippincott; 1992:75 - 79.
27. Magdeburg B, Fried M, Meyenberger C. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of anal carcinomas. Endoscopy. 1999;31:359 - 364.