Researchers present findings on promising biomarker for esophageal cancer
A new biomarker for esophageal cancer shows promise in improving screening for this deadly disease and its precursor, Barrett’s esophagus.
Amitabh Chak, MD, of University Hospitals Case Medical Center’s Seidman Cancer Center and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, presented findings today at Digestive Disease Week in Chicago in a research forum titled “Aberrant Vimentin Methylation in Esophageal Brushings: A Biomarker for Detecting Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma” (embargoed May 5, 9:15 am CT).
Dr. Chak and a research team found that a change in the DNA, methylation of the vimentin gene, can be an effective new less-invasive test for detecting Barrett’s esophagus (BE). In 117 patients, they examined if a new, non-endoscopic “brushing” of the esophagus is as effective as the more invasive, traditional biopsy.
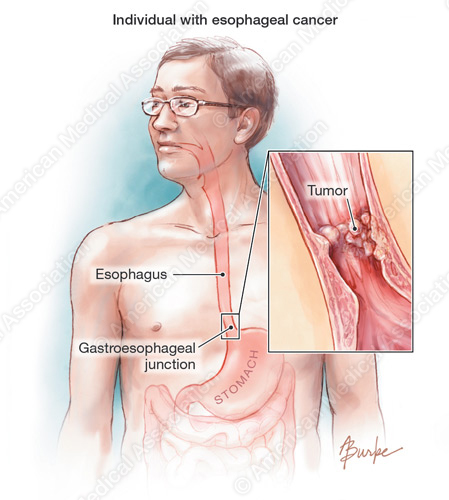
Affecting up to 6.8 percent of the population, BE is a leading predictor of esophageal cancer. Compared with the general population, patients with BE have an 11-fold higher risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
“Despite the fact that the rates of common cancers have declined in recent years, esophageal cancer has a poor five-year survival rate of less than 15 percent,” said Dr. Chak. “Early detection through screening can prevent the development of esophageal cancer. This promising new test has important clinical implications through its potential to improve screening and decrease mortality from this deadly disease.”
The research builds upon previous work by the team that aberrant vimentin methylation is a highly common epigenetic alteration in neoplasia of the upper gastrointestinal tract. In this study, they analyzed esophageal specimens in patients with BE, esophageal cancer as well as control subjects. The data determined that methylated vimentin is a highly sensitive biomarker for Barrett’s esophagus and that the less invasive brushing technique can effectively detect these changes in the DNA.
 The study is funded through the Barrett’s Esophagus Translational Research Network (BETRNet), a $5.4 million grant to Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. The five-year award supports a research team, led by Dr. Chak, collaborating to develop an understanding of the basis of Barrett’s esophagus and its conversion to esophageal carcinoma through genetic, molecular and physiologic studies.
The study is funded through the Barrett’s Esophagus Translational Research Network (BETRNet), a $5.4 million grant to Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine. The five-year award supports a research team, led by Dr. Chak, collaborating to develop an understanding of the basis of Barrett’s esophagus and its conversion to esophageal carcinoma through genetic, molecular and physiologic studies.
The study is collaborative with the National Cancer Institute’s Specialized Program of Research Excellence (SPORE) in Gastrointestinal (GI) Cancers award to the School of Medicine. The $11.3 million SPORE grant, led by Sanford Markowitz, MD, focuses on translational research aimed at reducing the incidence and deaths from colon and esophageal cancers. The study is additionally supported by the NCI’s Early Detection Research Network (EDRN) program that is also led by Dr. Markowitz, and is supported by a $1.5 million NCI grant to Case Western Reserve.
In vivo cancer biomarkers of esophageal neoplasia
The emergence of in vivo cancer biomarkers is promising tool for early detection, risk stratification, and therapeutic intervention in the esophagus, where adenocarcinoma is increasing at a rate that is faster than any other in industrialized nations. Exciting advances in target identification, probe development, and optical instrumentation are creating tremendous new opportunities for advancing techniques of molecular imaging. Progress in these areas is being made with small animal models of esophageal cancer using surgical approaches to induce reflux of acid and bile, and these findings are beginning to be evaluated in the clinic. Further identification of relevant targets, characterization of specific probes, and development of endoscopic imaging technologies are needed to further this direction in the field of molecular medicine. In the future, new methods that use in vivo cancer biomarkers for the early detection of neoplastic changes in the setting of Barrett’s esophagus will become available.
###
Lu S, Wang TD.
“Our team’s hope is that the use of molecular markers for non-endoscopic screening will drive down the cost and increase the ease of screening for these early esophageal lesions that can give rise to cancer,” said Dr. Markowitz, an oncologist at UH Case Medical Center Seidman Cancer Center and Ingalls Professor of Cancer Genetics at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine. “Longer term we hope to find additional markers that will allow the same approach to be used in the monitoring of Barrett’s patients to detect early progression to more advanced disease.”
Senior faculty collaborators on the research team included Dr. Chak, Dr. Markowitz and Joseph Willis, MD, Vice-Chair of the Department of Pathology at UH and the School of Medicine. First author on the report is Helena Moinova, PhD, instructor in the Department of Medicine at the School of Medicine, who was also assisted by James Lutterbaugh and Apoorva Chandar.
Epigenetic biomarkers in esophageal cancer
The aberrant DNA methylation of tumor suppressor genes is well documented in esophageal cancer, including adenocarcinoma (EAC) and squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) as well as in Barrett’s esophagus (BE), a pre-malignant condition that is associated with chronic acid reflux. BE is a well-recognized risk factor for the development of EAC, and consequently the standard of care is for individuals with BE to be placed in endoscopic surveillance programs aimed at detecting early histologic changes that associate with an increased risk of developing EAC. Yet because the absolute risk of EAC in individuals with BE is minimal, a clinical need in the management of BE is the identification of additional risk markers that will indicate individuals who are at a significant absolute risk of EAC so that they may be subjected to more intensive surveillance. The best currently available risk marker is the degree of dysplasia in endoscopic biopsies from the esophagus; however, this marker is suboptimal for a variety of reasons. To date, there are no molecular biomarkers that have been translated to widespread clinical practice. The search for biomarkers, including hypermethylated genes, for either the diagnosis of BE, EAC, or ESCC or for risk stratification for the development of EAC in those with BE is currently an area of active research. In this review, we summarize the status of identified candidate epigenetic biomarkers for BE, EAC, and ESCC. Most of these aberrantly methylated genes have been described in the context of early detection or diagnostic markers; others might prove useful for estimating prognosis or predicting response to treatment. Finally, special attention will be paid to some of the challenges that must be overcome in order to develop clinically useful esophageal cancer biomarkers.
Kaz AM, Grady WM.
 “This is true translational research, bringing a discovery from the laboratory to the patient care setting,” said Dr. Chak. “This new technique to sensitively detect changes in the DNA may have significant implication for the clinical practice of screening and primary prevention of esophageal cancer.”
“This is true translational research, bringing a discovery from the laboratory to the patient care setting,” said Dr. Chak. “This new technique to sensitively detect changes in the DNA may have significant implication for the clinical practice of screening and primary prevention of esophageal cancer.”
###
About University Hospitals
University Hospitals, the second largest employer in Northeast Ohio, serves the needs of patients through an integrated network of hospitals, outpatient centers and primary care physicians in 16 counties. At the core of our health system is University Hospitals Case Medical Center, one of only 18 hospitals in the country to have been named to U.S. News & World Report’s most exclusive rankings list: the Best Hospitals 2013-14 Honor Roll. The primary affiliate of Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, UH Case Medical Center is home to some of the most prestigious clinical and research centers of excellence in the nation and the world, including cancer, pediatrics, women’s health, orthopaedics and spine, radiology and radiation oncology, neurosurgery and neuroscience, cardiology and cardiovascular surgery, organ transplantation and human genetics. Its main campus includes the internationally celebrated UH Rainbow Babies & Children’s Hospital, ranked among the top children’s hospitals in the nation; UH MacDonald Women’s Hospital, Ohio’s only hospital for women; and UH Seidman Cancer Center, part of the NCI-designated Case Comprehensive Cancer Center at Case Western Reserve University. UH Case Medical Center is the 2012 recipient of the American Hospital Association - McKesson Quest for Quality Prize for its leadership and innovation in quality improvement and safety.
###
Alicia Reale
.(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address)
University Hospitals Case Medical Center