The relationship between impulsivity and Internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents
3. Results
3.1. Ongoing main Internet activities
According to the students’ self-report, the Internet was used mainly for virtual games (78.1%), chat room activity (14.2%), school-related activities (4.1%), and other (3.6%). There was no significant difference between the Internet Addiction group and the control group (P > 0.05).
3.2. Psychiatric comorbidity
Of the 2620 participants who fully completed the survey, 64 participants met the criteria for Internet addiction. Of the 64 participants with Internet addiction, 1 participant fulfilled DSM-IV criteria for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), 2 for conduct disorder (CD), 2 for oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), 1 for depressive disorder, and 8 for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
3.3. Comparison of impulsivity between Internet Addiction group and control group
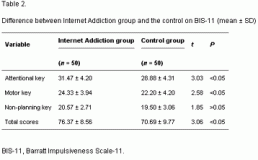
A comparison of average BIS-11 scores in the Internet Addiction group and control group is shown in Table 2. Compared to the control group, we observed significantly higher attentional key, motor key, and total scores for the Internet Addiction group (P < 0.05).
Table 2.
Difference between Internet Addiction group and the control on BIS-11 (mean ± SD)
 As can be seen in Table 3, there was significant difference between the groups’ ability to withhold responses. The Internet Addiction group demonstrated more difficulty withholding responses than the control group at the 50, 150, 250, and 350 stop signal delays.
As can be seen in Table 3, there was significant difference between the groups’ ability to withhold responses. The Internet Addiction group demonstrated more difficulty withholding responses than the control group at the 50, 150, 250, and 350 stop signal delays.
Table 3.
Difference between Internet Addiction group and the control on the number of failure to inhibit responses (GoStop) (mean ± SD)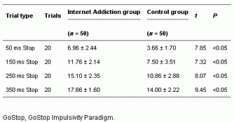
3.4. Relationship between Internet addiction and impulsivity
Pearson correlations were used to examine the relationship between YDQ scores and impulsivity level. Table 4 shows that, YDQ scores correlated positively with BIS-11 attentional key, motor key, and non-planning key scores. There was a significant positive correlation between YDQ scores and the number of failures to inhibit responses of GoStop. There was also a significant positive correlation between BIS-11 and GoStop scores. All correlations demonstrated statistical significance (P < 0.05).